5G is now available in most parts of the world, allowing for faster and more reliable mobile device communication. Which transformations will it trigger for customers and telcos?
Demand Side: 5G Will Enable New Mobile Innovations Which Make Up For 4Gs Weaknesses
We have long been expecting the arrival of 5G as the next generation of mobile cellular networks. Since 2019 large telecommunication companies have started deployments all over the world and are now offering high speed connections in many large metropolitan areas.
5G is based on four key technology changes compared to 4G (look at illustration 1, bottom up): It applies much higher frequencies than 4G. It uses more but shorter range towers across cities. It requires dedicated 5G equipment such as 5G phones, wearables, and routers to receive the new signal, and it is underpinned by even smarter software to control the vast array of beam connections and optimize the network traffic.
Compared to 4G, 5G will deliver a quantum leap in performance in terms of reach and throughput although the cost picture is mixed (see next section for a comparative analysis between 4G, 5G and fixed fiber connection). As promised, 5G will enable new business technology capabilities which can be applied in many industries, such as extended reality, large scale sensoring and control (Internet of Things) and autonomous machines.
Real value creation examples include:
- TV broadcasting: Prior to 5G, broadcasters were already experimenting with 4G cameras to limit the need for satellite trucks, cables and other fixed hardware. However, due to the limits in capacity and speed in 4G the technology was highly unreliable. With 5G's improved capacity and ability to steer dedicated beams to cameras, the technology is now being used to increase flexibility and mobility within broadcasting.
- Automotives: The precision and spatial awareness of autonomous vehicles and robots will improve. Enhancements in processing power and reduced latency within extended reality and other edge computing devices will vastly increase the usability.
- Logistics: Increased network efficiencies make it more feasible to add sensors to wearables, logistics assets and even in cities.
- Manufacturing: The industry has for a while been using different kinds of sensors and signaling devices to track performance. In this case 4G and other radio frequencies have been sufficient, however, 5G will extend the power capabilities of sensors to new levels.
- Healthcare: Enabling surgeons to operate remotely utilizing a screen, robotics and extremely low latency connection.
While some application areas might be visible soon, others are further into the future. We should also expect the technology to continue improving, enabling potentially new waves of applications. For example 5G latency still has some way to go and the research into the required supporting systems is still in its infancy.
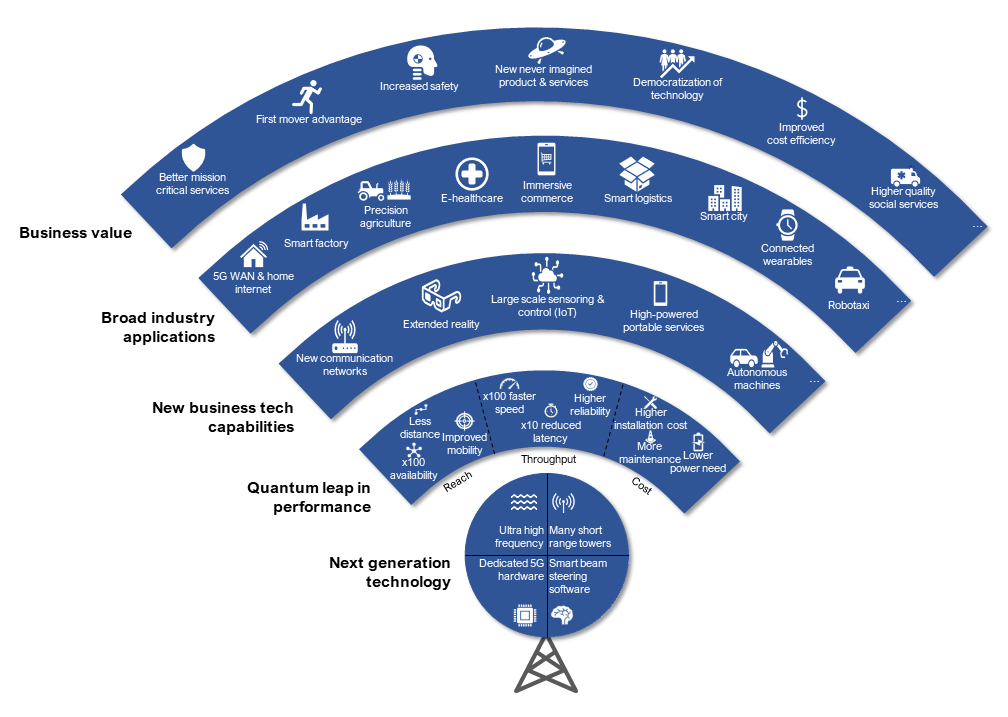
Illustration 1: How 5G creates value (compared to 4G). Analysis and illustration by Oleto Associates.
Supply Side: 5G Will Lift Telcos' Comms Offerings But Is Unlikely To Cannibalize Fixed Networks
5G technology is intended to replace 4G as the dominant mobile telephony technology, just like 4G is causing the phase out of 3G, thereby causing a self-imposed technology renewal on telcos. More realistically 4G and 5G will coexist for some time, with 4G providing long range connectivity and 5G shorter range, higher performance connectivity. In time 5G could completely replace 4G, also on the longer range.
But will 5G cannibalize the fixed fiber business or fixed broadband? To understand this we have qualitatively compared the reach, throughput and cost performance today (see illustration 2).
Based on this we believe it is unlikely that 5G will significantly cannibalize fixed fiber based networks, at least in the short to medium term:
- Many businesses and public institutions will continue to choose fiber as their mission critical way of communicating between sites. Fiber still outperforms 5G when it comes to speed and reliability. This makes it a greater risk for businesses where failure can have huge implications.
- The data volumes needed in the years to come are unlikely to be exclusively supported by 5G.
- Fiber will be needed to support the critical underlying connective backbone to support the 5G infrastructure.
But longer term we could see changes, as 5G could become more viable as an on-premise connectivity alternative for private households and small businesses customers, eating into the broadband market.
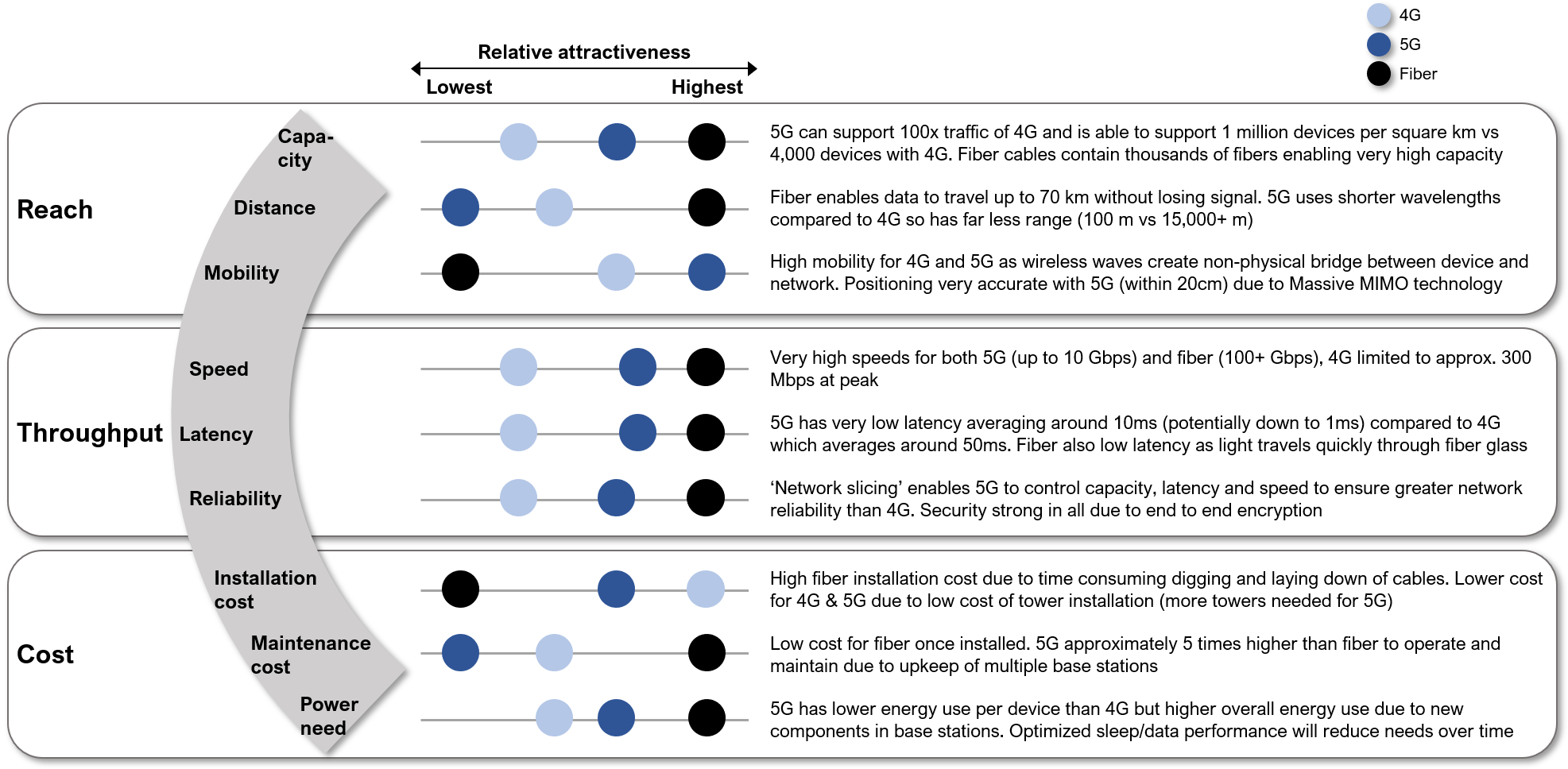 Illustration 2: Performance differences between 4G, 5G and fiber
Illustration 2: Performance differences between 4G, 5G and fiber
Ten Strategic Questions To Be Addressed
While it is uncertain how fast the wide adoption of 5G will happen in specific industries, it is important that organizations develop a perspective on the impact of 5G in their industry:
Five crucial questions every business leader (demand side) must be able to answer are:
- Q1: Where can we immediately create value from 5G by improving processes and product within our current business?
- Q2: How can 5G be used to radically improve our product offerings for current markets and where do we start?
- Q3: Can we use 5G to develop completely new offerings potentially creating new markets by disrupting traditional industry segments?
- Q4: Is 5G already thought into our digitalization strategy? How to we prioritize the many initiatives?
- Q5: What are the competitors likely move? Is our current industry in danger of being disrupted by external forces using 5G to develop new offerings?
For telcos (supply side) another set of five questions are:
- Q6: Which role do we want to play in the value chain, e.g., do we want to codevelop business solutions for our customers or do we need partners?
- Q7: How we transition from 4G and 5G, commercially and technically?
- Q8: How do we educate current and future customers on role of 5G versus fixed fiber?
- Q9: Which 5G based products should we introduce that could eventually cannibalize our broadband business?
- Q10: Which moves are our competitors likely to take and how to we position ourselves in that space?
About the authors: This article was written by a team of consultants from Oleto Associates, a strategy consulting firm based in Denmark. For more information please visit www.oleto.com
December 2020